Refrigeration System Types and Working Principle
Introduction of Refrigeration System
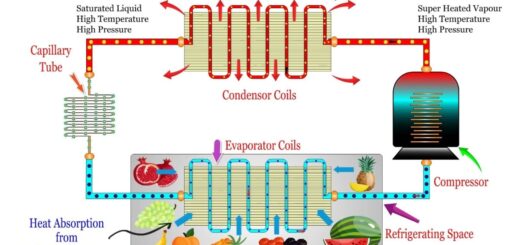
Refrigeration System Types and Working Principle :- Refrigeration is referred to as a process in order to achieve and maintain a temperature below that of outer atmosphere with an aim to cool some product or space to the required temperature.
One of the most important application for which refrigeration system is used, is the preservation of the perishable food products by storing them at a comparative lower temperature.
Refrigeration systems are most commonly used for providing the thermal comfort to the human beings so that the air conditioning can be utilized. Here, air Conditioning can be referred to as the treatment of the air in order to simultaneously control the temperature, moisture content, cleanliness, odor and circulation which is required by the occupants.
Types of Refrigeration System
1. Mechanical Compression Refrigeration System: ( Types of Refrigeration System )
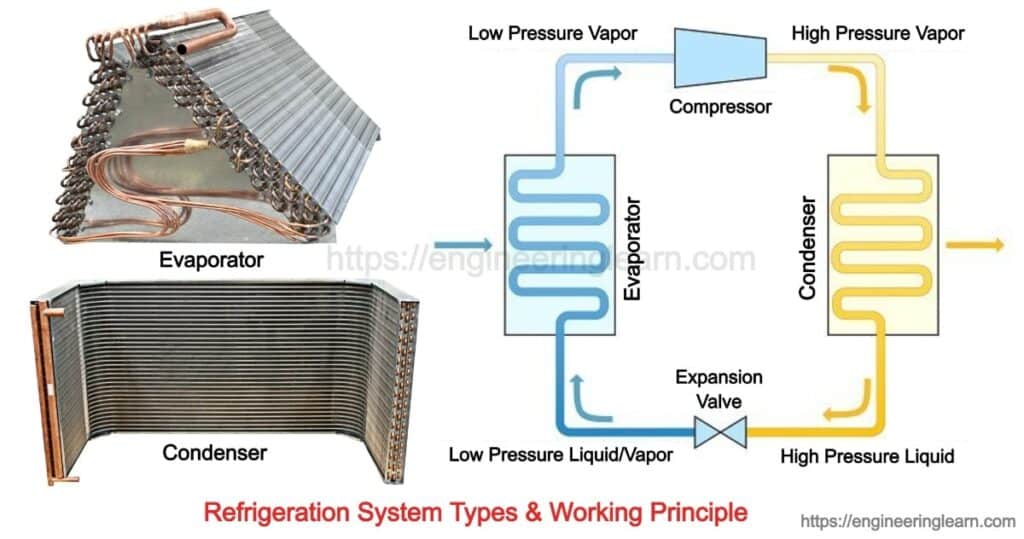
The mechanical compression refrigeration system is referred to as those system which is most widely-used in the refrigeration cycle method due to its multiple applications like air conditioning, commercial and industrial refrigeration etc. Most commonly these are the systems which are likely to transfer the heat by mechanically compressing the refrigerants into a quite low-pressure, cold liquid and by expanding it into hot or high-pressure gas. Once the heat is absorbed and released it the cool are is emitted and the hot air is condensed back into liquid.
2. Evaporative Cooling System: ( Types of Refrigeration System )
Evaporative cooling is quite different from the mechanical compression as it is traditional refrigeration cycle which has been followed from years. This was the technique which can cool the warmer outdoor air as well by the help of water-soaked pads by blowing it over your home or the required area. The water soaked pads work in the way that the water absorbs the heat from the air and evaporates once the cooler air is floated into the area after which the warm air is directed out of it.
3. Absorption Refrigeration System: ( Types of Refrigeration System )
Absorption refrigeration is referred to as a system in which the heat is also transferred by the process of compression and expansion refrigerant which is found to be quite similar to the mechanical compression. This is the kind of refrigeration system which relies on the process of absorption and heats in order to move the refrigerant which varies from the lower pressure side to the higher pressure side, rather of an electrically-powered mechanical compressor.
4. Thermoelectric Refrigeration System: ( Types of Refrigeration System )
Thermoelectric refrigeration systems is referred to as the most unique which because they do not use any water or refrigerant rather they use a thermoelectric refrigeration system wherein the thermocouple and the electric current does its job. The thermocouple is constructed of two different metal wires which is united at both the ends whereas the rest of the wires are separated by the insulation.
Thermoelectric refrigeration system is the system which works by using the Peltier effect in order to create a heat flux within the junctions of two different types of materials. This type of refrigeration system is most commonly used in camping, at places where portable coolers are needed and for also cooling the electronic components and small instruments.
Working of Thermoelectric Refrigeration System
By applying the DC voltage difference within the thermoelectric module, an electric current is found to pass through the module wherein the heat is absorbed from one side and is then released from the opposite side. Therefore, one module face is found to be cooled whereas the opposite face is heated simultaneously.
As soon as the current is directed to the thermocouple, its one end is found to become hot whereas the other end becomes cooler. Practically, the hot end is mostly placed outside the area which is to be cooled while the heat sink is attached to it in order to keep the same temperature as that of the surrounding air. Whereas the cooler side is placed in the area to be cooled which attracts heat from the air in order to make it perfect for small cooling loads which can be difficult to access like the electronic systems.