Cylinder Block Types and Functions
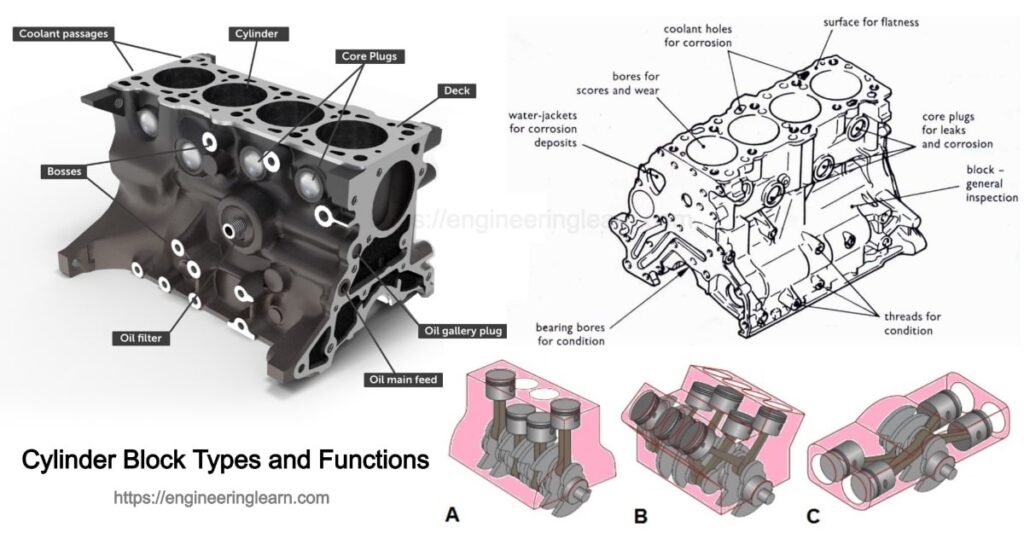
What is Cylinder Block?
Cylinder Block Types and Functions :- Cylinder block is the main stationary body of the automobile engine and it serve as foundation. They work as support and enclosure for moving parts. Now days, the cylinder block and crankcase casted together in single casting, which gives a rigid structure.
The cylinder block may also have a separate crankcase for the crankshaft, which is mainly confined to large engines and marine and stationary engines. A separate aluminum crankcase which is made of aluminum is preferred because of less weight, cheaper and quick replacement.
A cylinder block consists of three parts:
- The cylinders in which the piston slide up and down.
- The ports opening for the valves
- It provides jackets for heat dissipation by the flow of cooling water
Function of Cylinder Block
- The main function of a cylinder block is that it enclosed the connecting rod, piston and crankshaft. Their individual working takes place inside the block.
- It supports the other main components of the automobile engine and the auxiliary devices, such as A/C compressor, alternator, intake and exhaust manifold, etc.
- It consists lubrication mechanism components like oil pan, oil pump, oil filter etc.
- It also helps in the cooling circuit
Types of Engine Block / Types of Cylinder Block
Cylinder Block Types and Functions :- Engine blocks are classified on the basis of configuration of the engine cylinder. Following are the types of engine block:
1. V Engine Cylinder
It is the popular engine cylinder type and widely used now a days. In this configuration engines are arranged in two rows. The two rows are set an angle to each other. The angle V is kept small, usually 15° to 20°, because with larger angle the balancing of the engine becomes more difficult. This type of engine is rather difficult to balance with counter weights on the crankshaft.
The crankshaft has only two cranks, with connecting rods from opposing cylinders in the two rows being attached to the same crankpin. Every two connecting rod are attached to a single Crankpin. Different kinds of v engine are, for heavy vehicles V16, V8s and for small motorcycles V4s is used as cylinder block.
2. Inline Engine Cylinder
Inline engine cylinder block, a series of cylinders is arranged in a way that they run in a single line. Automobiles with this kind of engine block works smoothly; this is the reason why these are mostly used where high rpm is required. This is mostly used in passenger cars.
3. Opposed Engine Cylinder / Boxer Engine Cylinder
The boxer engine is basically the flat pressed V engine. In this cylinder blocks arriving two rows of two cylinders each set opposite to each other. This design is also known as pancake engine. This requires very little head room so that the engine, compartment can be very compact. The Volkswagen engine has this type of arrangement of 4 cylinders. It is air cooled and is mounted at the rear of the car. This engine block is also used on Porsche and Subaru and some other high engines.
Advantages of V engine Block over In-line Engine Block
- V engine block permits a shorter, lighter and more rigid engine. More rigid engine permits higher running speeds and higher combustion pressure with less difficulty from flexing or bending of the cylinder block and crankshaft. Flexing throws the engine out of line, increases frictional losses and wear, and may also set up internal vibrations.
- It permits the use of intake manifold that assures relatively even distribution of the air fuel mixture to all cylinders since all cylinders are relatively close together.
- It allows lowering of the hood line and which consequently lowers the car profile. This is because the carburetor and other parts are rested between the two rows of cylinders so they do not take up headroom above the cylinders.
Cylinder Block Problems
- The leakage of external engine coolant: This leak can happen by the water pump, radiator, heater core, or a loose hose. Sometimes it can be caused by engine block itself due to cracks.
- Worn/cracked cylinder: After long working time of the cylinders, wear inside cylinder is normal phenomenon. Dur to this smooth machined wall can be deteriorated. This effect the sealing by piston rings. This problem can be solved by increasing the bore size.
- Porous engine block: This engine block failure is generally caused by contaminant that enters the metal. It often happens during the manufacturing process. There is no solution of this problem as this problem is because the cylinder block is originated with it.
Image Source :- newkidscar, mechathon, howacarworks