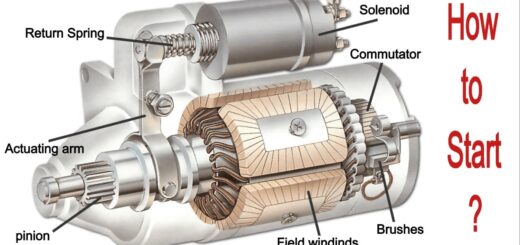
Types of Turbocharger
What is Turbocharger?
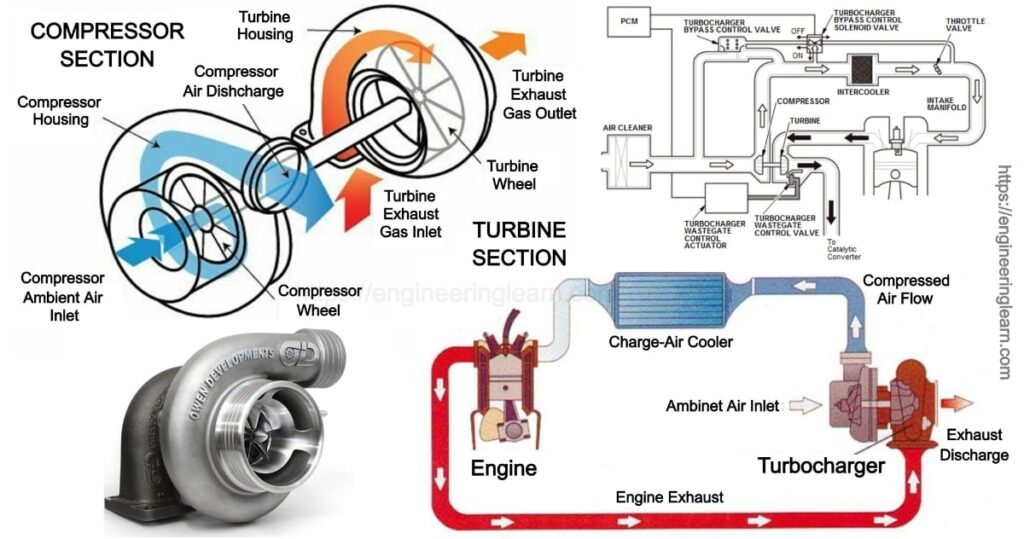
Types of Turbocharger :- A turbocharger unit is referred to as that unit which comprised of two main components, first is the turbine and second is the compressor. The main purpose of a turbocharger is to increase the volumetric efficiency of the combustion chamber. The compressor of the turbochargers is found using air from the atmosphere which is responsible for increasing the density through the rotation of impeller blade passages.
The turbine of the turbocharger is responsible for producing high back pressure on the exhaust manifold which results in the higher exhaust gas pressure as compared to the atmospheric pressure.
Types of Turbocharger
There are 6 different types of turbocharger which is commonly known within the automotive industry and are mentioned below:
- Single-Turbo
- Twin-Turbo
- Twin-Scroll Turbo
- Variable Geometry Turbo
- Variable Twin Scroll Turbo
- Electric Turbo
1. Single-Turbos: (Types of Turbocharger)
Single turbochargers are referred to as those turbos which are mostly thought by most of the people that exist with varying size of the elements within it and which is completely different in terms of torque and its characteristics can also be achieved. If the turbos are larger than it will surely provide higher levels of top end power whereas the smaller turbos can spool faster and can also provide better low-end power.
It is found to be a cost-effective way by which the power of the engine can be increased and have become very commonly known which allows the smaller engines to increase its efficiency by producing the same power as done by the larger and naturally-aspirated engines with a lower weight. These turbos tend to work best within a limited RPM range and also the drivers are found experiencing turbo-lag until the turbo gets started and comes in an operating condition with its rev band at the peak.
Advantages of Single-Turbos
- In comparison to others this is quite cost effective way by which the power of the engine is increased and the efficiency as well.
- Quite simple and is usually the easiest method of turbocharging with various installation options.
- It can be used by the smaller engines in order to produce the same level of power as produced by the larger naturally-aspirated engines which are found removing weight.
Disadvantages of Single-Turbos
- Single turbos tend to have a quite arrow effective RPM range which makes sizing a major issue, as there is a need to choose between good low-end torque and better high-end power.
- The response of turbo may not be that quick as compared to the turbo setups.
2. Twin-Turbo: (Types of Turbocharger)
Quite clearly predicted by the name that the twin-turbos are found with an additional turbocharger to an engine. Considering the case of V6 or V8 engines, these are assigned with a single turbo to work with each cylinder bank. Other than this, a smaller turbo is used at comparatively lower RPMs with a quite larger turbo for higher RPMs.
The twin sequential turbocharging also provides for a wider range of RPM operations and also provides better torque at lower turbo lag. This helps in giving power at high RPMs. The two turbos are also used with an aim to increase the complexity and the cost associated to it.
Advantages of Twin-Turbo
- In case of parallel twin turbos in ‘V’ shaped engines, the benefits and the drawbacks are quite similar to the single turbo setups.
- For sequential turbos or for using a turbo at low RPM and both at high RPM, it provides a much wider and flattered torque curve accompanied with a better low-end torque wherein the power does not get tapered at a high RPM with a small single turbo.
Disadvantages of Twin-Turbo
- Cost and complexity is its biggest disadvantage.
- In comparison to others these are quite lighter with more efficient ways of achieving similar results.
3. Twin-Scroll Turbo: (Types of Turbocharger)
Twin-scroll turbochargers refers to as those turbocharges which require a divided-inlet turbine housing and exhaust manifold that is found pairing the correct engine cylinders independently. For instance, considering a case of a four-cylinder engine, with a firing order 1-3-4-2, cylinders 1 and 4 can feed to one scroll of the turbo, whereas the cylinder 2 and 3 can feed to a separate scroll.
This layout helps in providing a highly efficient delivery of exhaust gas energy to the turbo which results and helps in providing a highly dense and pure air into the cylinder. The higher the amount of energy is sent to the exhaust turbine, higher will be the power generated. In these type of turbo it is found that there is a cost penalty for addressing the complexity of a system which requires a complicated turbine housings, exhaust manifolds and turbos.
Advantages of Twin-Scroll Turbo
- The higher the amount of energy is sent to the exhaust turbine, higher will be the power generated.
- A very high RPM range of effective boost is possible which is based on the different scroll designs.
- More valve overlap is possible which is possible without hampering the exhaust scavenging, which clearly predicts more tuning flexibility.
Disadvantages of Twin-Scroll Turbo
- It is found that there is a requirement of a specific engine layout and exhaust design which can be fed to each scroll of the turbo, at even intervals.
- Cost and complexity is more as compared to the traditional single turbos which makes it tedious to maintain.
4. Variable Geometry Turbo: (Types of Turbocharger)
VGTs refers to as those types of turbochargers which include a ring of aerodynamically-shaped vanes inside the turbine housing at the turbine inlet. The turbos used in the passenger cars and light commercial vehicles, can rotate in order to vary the gas swirl angle and the cross-sectional area simultaneously. The internal vanes which are present alter the turbos area-to-radius ratio (A/R) in order to match the RPM of the engines, and to also give a peak performance.
Considering a case of low RPM, a low A/R ratio occurs which helps the turbo to spool up quickly by increasing the velocity of the exhaust gas. At higher revs the A/R ratio increases which is responsible for the increased airflow. This results in a low boost threshold which is responsible for reducing the turbo lag, and also provides a wide and smooth torque band.
While the VGTs are quite typically used in the diesel engines where the exhaust gases lower the temperature and by then the VGTs were just limited in the petrol engine applications due to their cost and the requirement for components was made from an exotic material. The higher the temperature of the exhaust gases predicts that the vanes should be made from an exotic heat-resistant material which is used to prevent damage. This has been restricted to their use within luxury and the high performances of the engine.
Advantages of Variable Geometry Turbocharger
- Quite wide and flat torque curve. It is an effective method of turbocharging with a very wide RPM range.
- It just requires a single turbo which simplifies a sequential turbo setup into more compact.
Disadvantages of Variable Geometry Turbocharger
- These are most used in the diesel applications where the exhaust gases are lower so that the vanes will not be damaged by the effect of heat.
- For gasoline applications the cost keeps them out and have to be used in order to maintain reliability. The tech was used in the Porsche 997, although very few VGT gasoline engines exist as a result of the cost associated.
5. Variable Twin-Scroll Turbo: (Types of Turbocharger)
The name completely suggests that a VTS turbocharger refers to as that turbocharger which combines with the advantages of a twin-scroll turbo and a variable geometry turbo. This is done by the use of a valve which can redirect the exhaust airflow in a single scroll or simply by varying the amount of the valve which gets opened and can be allowed for the exhaust gases in order to split into both scrolls.
The design of the VTS turbocharger is found having a cheaper and higher robust alternative to VGT turbos which means that it is a viable option for the petrol engines. This is the reason why it was preferred more in the petrol engines as compared to the diesel engines.
Advantages of Variable Twin-Scroll Turbocharger
- Comparatively quite cheaper than the VGTs, which makes an acceptable case for gasoline turbocharging.
- It allows a very wide and flat torque curve.
- These turbochargers are quite robust in the design as compared to a VGT which depends on the material selection.
Disadvantages of Variable Twin-Scroll Turbocharger
- Cost and the complexity were considered using a single turbo or a traditional twin-scroll.
- The technology has been played with before which does not seem to catch on in the production world. These are mostly the additional challenges with the technology.
6. Electric Turbo: (Types of Turbocharger)
An electric turbocharger is referred to as that which is used to eliminate the turbo lag and to also assist a normal turbocharger at a comparatively lower engine speeds wherein the conventional turbo is not that much efficient. This is done by the addition of an electric motor which is responsible for spinning up the compressor of the turbo from starting and through the lower revs, until the power from the exhaust volume is highest to make the turbocharger work.
This method makes the turbo lag and also increases the RPM band through which the turbo will be operated with even higher efficiency. It also appears as an electronic turbos which are the perfect answer to all the negative characteristics of conventional turbochargers, whereas there are some disadvantages too. Most amongst these are around the cost and its complexity as the electric motor should be accommodated and powered and should also be cooled to prevent the reliability issues.
Advantages of Electric Turbocharger
- The turbo lag can be prevented by directly connecting an electric motor to the compressor wheel. The insufficient exhaust gases produced can virtually eliminate the spinning compressor with the electric power whenever needed.
- The energy which seems to be wasted can be recovered by connecting an electric motor to the exhaust turbine.
- A very wide effective RPM range with torque all over.
Disadvantages of Electric Turbocharger
- Not economical and highly complex electric motor which keeps it cool in order to prevent the reliability issues which goes for an added controllers as well.
- Packaging and weight become an issue in case of an additional battery on board, which is necessary in order to supply the sufficient amount of power to the turbo whenever needed.
- Twin-scrolls are found offering a very similar benefit although not at the same level but over a significantly lower cost.
Advantages of Turbocharger
It is important to know that there are various advantages of turbocharger. Let’s dive in to learn more:
- The turbocharger are more powerful as compared to the naturally aspirated engines.
- Higher thermal efficiency as compared to naturally aspirated engine and supercharged engine as the engine exhaust is being used to do the useful work which would have been wasted
Disadvantages of Turbocharger
Knowing just about the advantages is not sufficient, so let’s learn what all can be the disadvantages of a turbocharger:
- In case the turbo is huge, the boost is built up slowly with more exhaust pressure which is needed to overcome the rotational inertia on the large turbine in order to reduce the throttle response.
- If the turbo is too small the turbo lag would not be as big, whereas the peak power would be quite less
- Complex turbocharger are found spinning with higher revolutions, proper cooling and lubrication is highly essential.