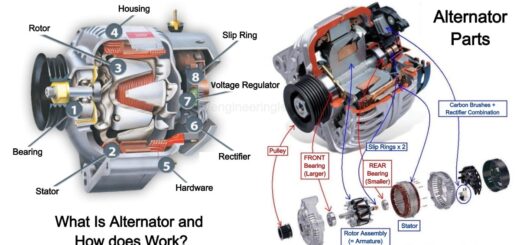
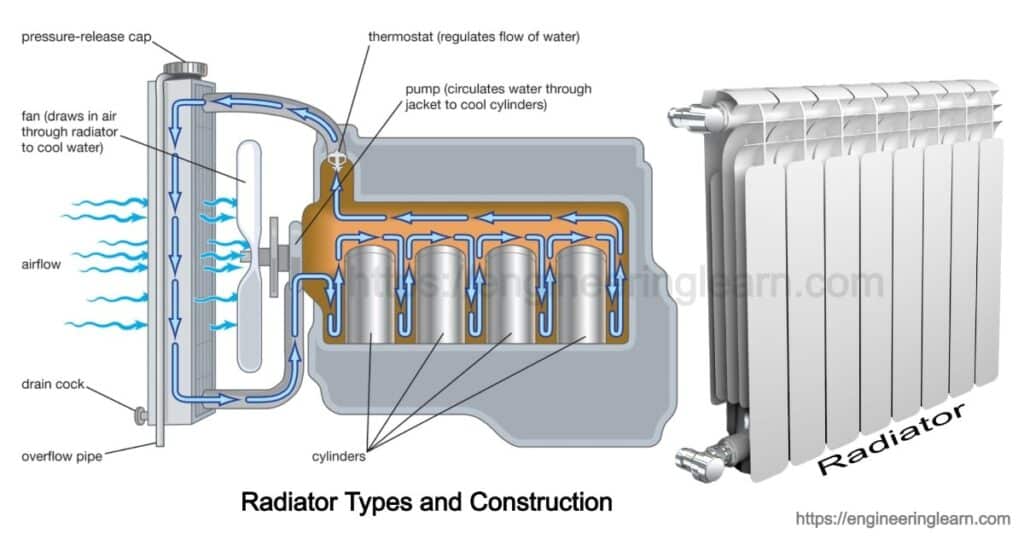
Radiator Types and Construction
What is Radiator?
Radiator Types and Construction :- In common language, the radiators are referred to as heat exchangers which are used to transfer the thermal energy from one medium to the other with a purpose of cooling and heating. A radiator consists of a large amount of cooling surface which contains a huge quantity of air that gets spread through the effect of water in order to cool down.
The radiator is found having a wide range of application in an automobile industry as there are various uses that cool the temperatures of an internal combustion engine in the automobile. These are popularly used in piston-engine aircraft, motorcycles and stationary generating plants. The material used in making of a radiator is usually copper and brass due to their high heat conductivity.
Types of Radiator
It is important to know about the types of radiator. So scroll down to know about the two types of radiators.
- Tubular type
- Cellular type
1. Tubular Type Core
The tubular type core radiators comprises of the upper and the lower tanks which are connected with a series of tubes which is used for passing water. Fins are usually placed across the tubes in order to improve the transfer of heat.
As water passes through all the tubes in a tubular radiator even if one tube gets clogged, the effect of cooling for the entire tube is lost. The tubular radiator type is constructed from steel which is then powder painted and is mounted with a stainless tubular heating element that is joined in an insulating plate.
It is advised that this type of radiator should only operate in high power as it becomes too hot on the surface. Also it should be equipped with a protection grate.
2. Cellular Type Core
The cellular type core is the radiator wherein the air passes through the tubes and the water flows through the spaces available between them. The core consists of a large number of individual air molecules which are surrounded by the effect of water and due to its appearance, the cellular type is usually known as a honeycomb radiator.
Construction of Radiator
The construction of a radiator consists of the below mentioned components which work in order to make a radiator efficient.
- Upper Tank
- Lower Tank
- Tubes
- Filler Cap
- Fins
1. Upper Tank: (Radiator Types and Construction)
The coolant gets heated by absorbing the heat of the engine, wherein the liquid expands and creates pressure in the radiator exceedingly. This pressure is responsible for causing the coolant to get higher as compared to the pressure cap which is important to prevent the leakage of the excess coolant which needs to be captured safely. The fluid which is in excess flows into the pipe and then moves into the overflow tank.
The engine of the vehicle emits heat which is settled by the action of the coolant. After this the coolant gets contracted instead of expanding which results in increasing the volume of the coolant. The effect of vacuum takes place wherever the pressure is found decreasing and allows easy excess of the coolant in the overflow tank so that it can back and then it can return to the radiator. The material of the tanks could be brass, plastic, polyamide etc.
2. Lower Tank: (Radiator Types and Construction)
Once it has been passed through the tubes which radiate heat, the fins in the body of the radiator the bottom tank receives the cooling water.
When it attains a significant temperature then the thermostat releases water at 180 degrees Fahrenheit. The water is found losing 100 degree Fahrenheit depending upon the ambient air temperature and the efficiency of the radiator meanwhile it reaches the bottom tank. The water pump holds this cooled water as a back-up which can get back in the block when it is again heated up.
3. Tubes: (Radiator Types and Construction)
When it is on its way to the opposite tank, the coolant gets passed through the radiator tubes. This is how it transfers heat to the tubes that transfer the heat to the fins which are attached amongst the rows. The head of fins transfers the heat flow to the ambient air.
The tubes of radiator are mostly made up of brass. The use of aluminium increases over the vast majority of vehicular radiator applications.
4. Filler cap: (Radiator Types and Construction)
When the coolant expands the high temperature of the coolant leads to an increase in the pressure in the cooling system. The coolant is supressed in the tank which increases the amount of pressure in the tank.
There is a pressure relief valve which is used to open the filler cap, which allows the air to escape. The partial vacuum which is formed in the cooling system whenever the coolant temperature reaches to normal it causes a vacuum in the tank as the Coolant gets extracted from the tank.
5. Fins: (Radiator Types and Construction)
Fins are referred to as the surfaces which are used to increase the rate of to or fro heat transfer from the environment which is then extended from the surface by increasing the convection. Fins on the other hand also increase the surface area which can be an economical solution to transfer problems of heat.
Working Principle Of A Radiator
- The radiator is a quite simple device mostly made of aluminum. Radiators usually consist of a tank on the either side or inside the tank of a transmission cooler. Mostly these types of radiators are found having an aluminum mesh.
- This aluminum device consists of two ports first is the inlet and second is the outlet port. The interior of the radiator comprises of tubes which are mounted in a parallel arrangement in which the aluminum fins are attached to all the tubes.
- The working of a radiator is not typical. The coolant moves from the inlet port to the outlet outlet and then passes through many tubes which are mounted in a parallel arrangement, in a radiator. The hot water goes into the radiator through the inlet port where a fan is attached behind the radiator to cool down the hot water in the tubes. The fan is installed to blow the air, to cool down the water. Therefore, the cooler water comes out which had entered before and then goes back to the engine.
- The fins of aluminum are attached to the tubes which are termed as tubulator. The tubes are filled with hot coolant which comes from the engine. This makes the heat go off from this aluminum coat by passing the air through the fan which is responsible for cooling down the aluminum coat. In case the fluid flows very smoothly through the tubes, then only the fluid touching the tubes would be cooled directly. After this it gets cold and then back to the engine.
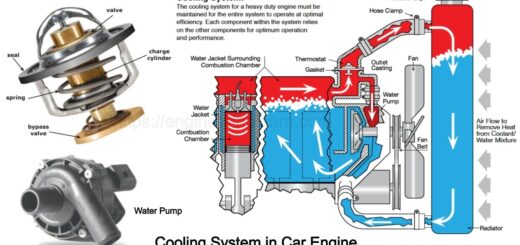
Cooling System in Engine
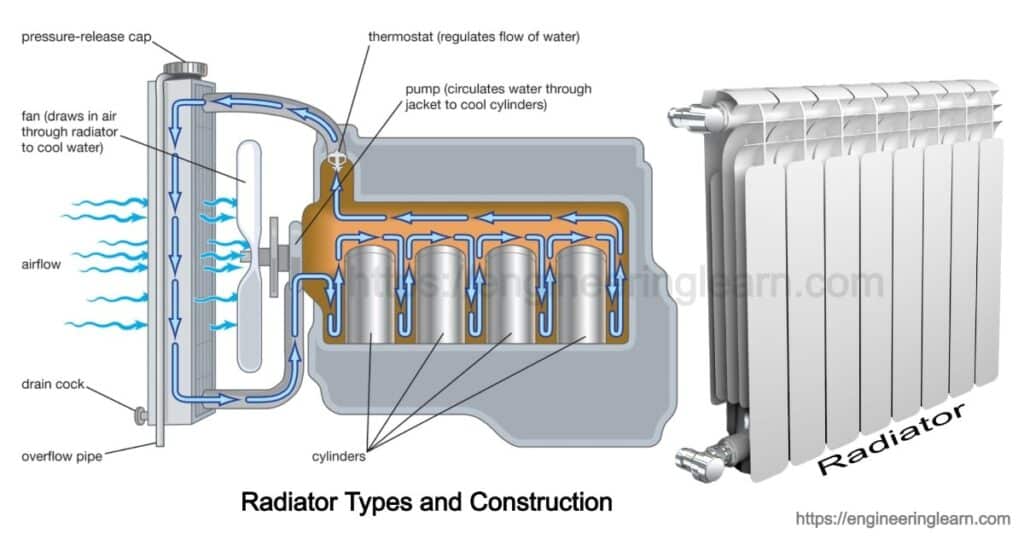
Here you will get to learn how a radiator gets cold which is installed in the front side of the car. The front side of the car includes an engine, a water pump and a thermostat. Once the car is started, the coolant starts running through the engine and as the engine warms up the coolant starts getting heated and the hot coolant is send to the radiator in order let it cool down. Once it gets cool, then the coolant goes back into the engine.
1. The Fan
The fan is usually mounted at the backside of the radiator on the water pump shaft. Once the engine runs at a low speed it can certainly be insufficient to produce the desired cooling from the nature. This is the main purpose of a fan. This is one of the most important component which plays a vital role in cooling the engine.
2. Thermostat
The thermostat is responsible for cooling the coolant which runs through the engine. Once the temperature of the coolant is increased and the engine is warmed up then the thermostat is responsible for detecting it and then it passes the coolant back through the radiator after which the coolant will cool through the radiator. This is how a thermostat is used to detect the temperature and work to decrease its temperature.
3. Water Pump
The water pump is used to increase the velocity of the water which is circulating. Once the low-temperature coolant passes through the water pump it pumps the coolant back into the engine. This is how a water pump works in cooling the engine and the coolant.
You Can Drive a Car Without Radiator?
A car can work without a radiator but on the other end is quite risky and is not suggested. The car is safe until the engine is not heated or over heated. In case you do not run it on longer routes for the engine to get too hot, then it is not at all an issue but in case the car gets overheated you will have to immediately shut down the car and let it to cool off.
Talking about the theory, the radiators are completely optional as air cooled engines have existed for a very long period. These radiators comprises of cooling fins which are used to extract the heat and release it into the air. Whereas, in case the car is designed to require a radiator one would definitely need one so removing it won’t be beneficial.
What Cause of Overheating Engine?
Overheating in an engine is caused due to an insufficient quantity of water present in the cooling system. One more reason for overheating is the clogged radiator condition which does not let the water pass, belt slipping, imperative thermostat, late ignition timing, incorrect valve timing, pre-ignition, bearing being too tight, low engine oil, clogging of the exhaust system etc.
How to Recognize a Bad Radiator?
- If the coolant is unable to get to the engine it might get heated which can be a sign that the radiator is not working.
- The hoses can be clogged or sometimes the level of the coolant can also be too low.
- You can find a warning light on the dashboard which can indicate the temperature gauge being too hot.
- If there is a broken hose or in case the radiator gets corroded or rusted, you may notice the smell of antifreeze or a tell-tale puddle on the garage floor.
- If the smoke is found from beneath the hood, it is possible that the coolant might have leaked into the motor which might get burnt off.
- If the smoke is observed coming out from the muffler, it is possible that the head gasket has been damaged from the heat of the engine.
Merits Of Radiator
Here are some of the merits of a Radiator which are mentioned below. Scroll down to know more:
- The radiator is of good heat dissipation. It obviously saves material and energy.
- Good performance of oxidation corrosion resistance
- They are highly responsive.
- They are environmentally friendly so they pollute less.
- They are easy to mould and thus can various design patterns.
- Materials like ceramic, cast iron are used to construct a radiator which holds the heat.
Demerits of Radiator
Knowing the merits are not sufficient, therefore one must know about the demerits of a radiator which are as follows:
- The loss of energy takes place in the form of heat if it is not maintained properly.
- The operations are highly noised.
- It needs an adequate amount of airflow so that the radiator can work properly.
- The heats from the unit gets trapped around the unit which decreases the comfort levels within your home and creates drafts and cold spots.
- Radiators can get extremely heated which cannot be touched while working. Therefore, it should be avoided from the pets and kids while the radiator is in running.
Applications Of Radiator
For a learner it is very important to know the usage as well as the application of Radiator. So scroll down to know some of the most common applications of radiator:
- To cool the oil present in the motor or the fluid of power steering.
- Used in automatic transmission fluid.
- Used in air conditioners and automobiles.