Piston Rings Types And Function
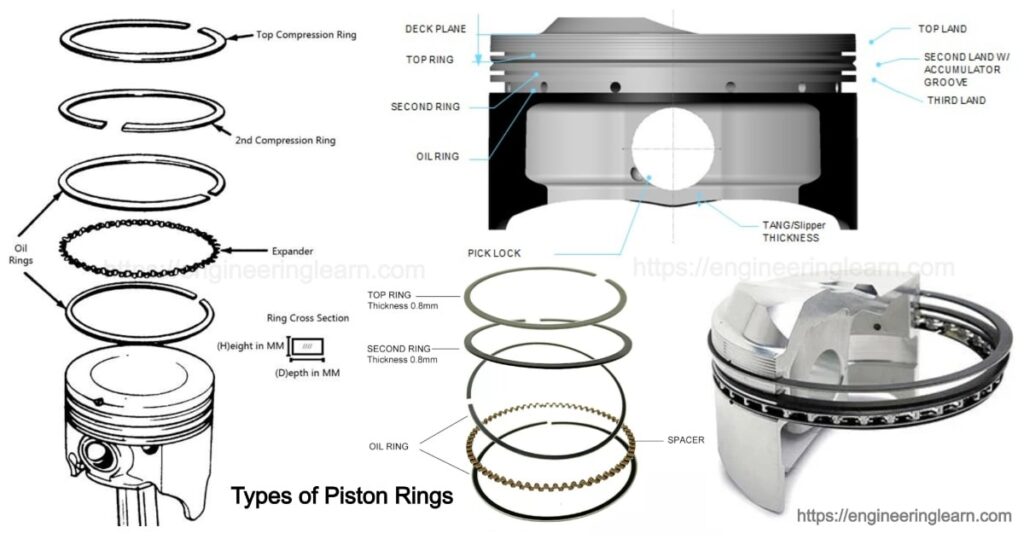
What is a Piston Ring?
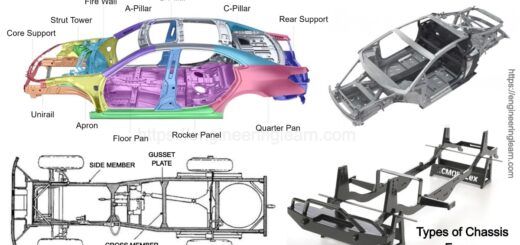
Piston Ring Types And Function :- The piston rings are metallic split type rings which are fitted into the grooves of the outer diameter of a piston in an IC engine to maintain good deal between piston and cylinder wall. Generally 3 to 4 rings are used in an IC engine.
Function of Piston Rings
- It provides a pressure seal for burnt gases so that they cannot enter into the crankcase.
- They provides path for heat conduction from piston crown to cylinder walls.
- They control the flow of oil to the skirt and prevent mixing with gases inside combustion chamber
Types of Piston Rings
There are two types of piston rings;
- Compression Rings
a) Counter bored and scrapper rings
b) Headland rings - Oil control Rings
1. Compression Rings: ( Types of Piston Rings )
There is generally two or three compression rings fitted on the piston. The number of compression rings depends on the compression ratio.
Generally 2nd and 3rd compression rings are taper-faced. These are used to overcome ring-sticking problems in high power engines.
In many cases oil control rings have a series of slots which transfer excess oil through holes in the piston groove to the inside of the piston and to sumps but leave sufficient amount of oil fro lubrication of cylinder walls. Oil rings give slightly more radial pressure on cylinder walls than compression rings.
A) Counter Bored and Scrapper Rings
Counter bored and scrapper rings are generally used for top and second compression rings. During suction stroke these rings are tend to twist slightly as a result of internal forces produced by cutting away corner rings.
During the compression stroke when piston goes upward rings also moves upward and they tend to stake on the oil film inside the cylinder wall. Thus less amount of oil is delivered into the combustion chamber.
During power stroke pressure force due to combustion causes to untwist the rings, as a result they have full contact with the cylinder walls for effective sealing.
B) Headland Rings
Headland rings are special kind of compression rings. They have L- shaped cross section. It covers the headland area of piston. This area has some amount of unburnt air fuel mixture.
After cooling, this unburnt mixture can produce smog. By use of headland rings this can be avoided and unburnt mixture is exhausted. These rings provide good sealing during power stroke. It increases horse power by 10%.
The headland rings also has an advantage of good sealing during power stroke. As. Combustion starts, the pressure acts quickly on the upper lip of the ring, forcing out thus having good sealing with the cylinder wall.
2. Oil Control Rings: ( Types of Piston Rings )
In some IC engines spilt he inside connecting rod splits oil from the oil pan during each revolution. As a result excess oil reaches on the cylinder wall than actually needed. It must be scrapped off and returned to the oil pan. Otherwise it will go to combustion chamber and burn. Thus oil consumption will increase and engine requires frequent oil refilling. Inside cylinder walls oil removal is as important as cooling, sealing and clearing. There are three types of oil rings
(i). One piece slotted cast iron type: – it has slots between the upper and lower faces of cylinder. The expander spring increases the pressure of the ring on the cylinder wall to improve scrapping effect.
(ii). One piece pressed steel type: – these mostly used in worn cylinder walls of engines. It is made of steel. It can seal one side of the groove.
(iii). Three piece steel rail type with expander: – it provides sealing in both directions i.e. upward and downward. Thus these are more effective in sealing.
Material Used For Piston Rings
The most commonly material used for piston rings is fine-grained alloy cast iron. Cast iron has self lubricating property because of graphite present in it which helps in less friction in cylinder liners and rings.
The piston ring material should be harder than cylinder liner for maximum life. Commonly used alloys in cast iron are nickel, chromium, titanium, copper, vanadium and molybdenum. Pressed steel is also used to make piston rings.
1. Piston Ring Gap
Piston rings are provided a gap so that they can be installed and removed from piston grooves when they worn out by expanding them. The radial pressure generated due to gap ensures the effective sealing to prevent leakage under heavy pressure.
The gap provided should be optimum means not very low or not high. The range of gap is 0.178-0.50mm and if the piston size is larger than gap is increased 1mm per 100mm increase in diameter.
The gap between ring and grooves should be in range of 0.038-0.102mm for compression rings and a little less for oil control rings. During the service ring may have lost some of its elastic properties due to which radial pressure will be reduced on the cylinder wall. They can be checked by comparing the gap between new and old rings.
2. Ring Coating
Piston rings are subjected to frequent loading conditions and high temperature, hence they wear out rapidly. Thus various coatings are used on the compression rings.
Relatively soft substances like phosphate, graphite and iron oxide are often used for coating of rings. Ring coatings also have good oil absorbing properties. They easily soak up oil and thus improve ring lubrication. They also prevent ring scuffing. Scuffing is the result of metal to metal contact at high temperature. It is a welding like phenomenon. The coating prevents such scuffing so weld cannot take place as there is no exposed part of iron.
The rate of wear in the cylinder bore can be considerably reduced by chromium playing the ring rather than the bore. (Piston Rings Types And Function)