Types of Chain Drive: Mechanism, Uses, Design, Applications, Advantages & Disadvantages

What is Chain Drive?
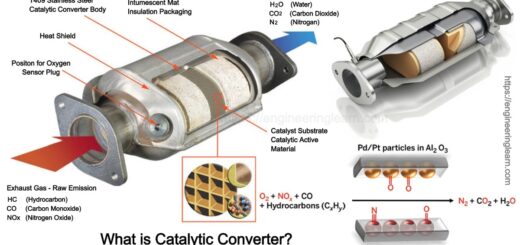
Types of Chain Drive: Mechanism, Uses, Design, Applications, Advantages & Disadvantages :- Chain drive can be defined as the way by which mechanical power is being transmitted from one place to another. Generally it is used for conveying power to the vehicle’s wheel especially in motorcycles and bicycles. They are also used in several of machines.
With the help of roller chain the power is conveyed and the roller chain are known as transmission chain or drive chain, by passing it through a sprocket gear and the teeth of gear mesh in holes of chain link. The sprocket gear is then turned which results in pulling the chain providing mechanical force to the system.
General Description of Chain Drives
The chain drives are simply oval loop in shape and can go around corners by providing more number of gear (it must be more than two). When a gear does not provide power to the system or does not transmit power are called idler wheels. Gear ration are altered by just varying the diameter of output and input gears with respect to each other.
For more torque and power to be transmitted, there is a chain known as duplex chain in which there are two chains which are joined side by side. Generally chains drive use teeth for transferring the motion in between the rollers and chain which leads to reduction of frictional losses as compared to the belt drive. Drive chains are commonly made of metal therefore they are heavier and have high inertia.
Design of Chain Drive
Chain drives are used for various of application and work on a large range of loads as well as speeds. The dimension of the chains is in proportion with one another and overall size of chain changes. There are various of chain variable but the major are width, pin diameter, pitch and thickness of link plates.
1. Pitch
Pitch is defined as the length between link plates and the Centre of the holes. Pitch defines the sprocket teeth.
2. Width
Width can be defined as inner link plates distance. Approximately width is 5/8th of link pitch.
3. Pin Diameter
It is the diameter of pin which is connecting outside and inside of the link plates together. Approximately it is 5/16th of link pitch and are ½ of roller diameter size.
4. Link Plate Thickness
The outer and inner link plates are of same thickness which is generally 1/8th of link pitch.
Types of Chain Drive
1. Roller Chain: ( Types of Chain Drive )
Roller chains are the chain which is commonly used for mechanical power transmission on various types of industrial, domestic, agriculture machinery, conveyors, printing presses, motorcycles, cars bicycles and tube and wire drawing machines. Roller chain has series of short cylindrical rollers which are held with each other by side links. They are driven with the help of a toothed wheel which is known as a sprocket. They are reliable, simple as well as efficient for the transmission of power.
These chains are also used as guide for supporting the material which is carried on it on the ways or tracks. Roller chain is used for conveyors as well as drive applications.
Single strand standard series roller chains are generally used for the drives
- Because they have wide range of power rating capacities for drive load requirements.
- For increased power capacity, multi strand roller chains are used which reduce the requirement of providing more chain pitch or linear speed.
2. Silent Chain: ( Types of Chain Drive )
They are also known as inverted tooth chain which has series of toothed link plates which are assembled together on joint components in such a way which allow free flexing between each pitch. They have flat link plates in addition with gear a type contour which is designed for engaging the sprocket teeth in same manner rack engages gear. Which the help of one or more pins at each joint the links are held together which also permits the chain to flex.
High performance silent chains have huge range of sizes with in widths and pitches and they are used for very high speed drives in which extra quietness and smoothness are required. Generally they are used for industrial equipment in which the requirement of smoothness is ultimate.
3. Leaf Chain: ( Types of Chain Drive )
These chains are used for the purpose of lifting instead of power transmission. They have slow speed but tensions are very high. Generally these chains work intermittently. Joint wear, sheave wear, link plate and tensile loads are the main consideration for the design of leaf chains.
They do no mesh with sprockets because they are run over sheaves therefore there is no chances for chains to get engage with sprocket. They need high yield strength for carrying large loads and not to be stretched permanently while carrying large loads. The common use of leaf chains are in lift trucks.
4. Flat Top Chain: ( Types of Chain Drive )
Flat top chains are generally used in conveyors, especially in various slat conveyors. Flat top chains have series of steel top plates in which they have hinge like barrels which is curled on each side. For making joint, pins are inserted via barrels and these act as a bearing as well as beams. Pins are retained at their place by heading in barrels on top plate or by press fits.
The pin which is used for connecting are generally enlarged on at one end for retaining the pin on one barrel at the top plate or knurled therefore a flat top chain of continuous length is formed and the flat top chain are used only for conveying.
5. Engineering Steel Chain: ( Types of Chain Drive )
These chains are developed in 1880 and are used for conveying applications which are difficult. Generally many steel chains are used by bucket elevators, tension linkages and conveyors and very few of them are used for drives. Tensile loads, lubrication and several types of wear are the main consideration for engineering steel chain.
Wear are very significant parameter for the design of engineering steel chain.
Style of chains used in chain drives is:
- Straight link chains: In this chain link there are alternate inside and outside links.
- Offset link chains: In this type of chain link, all links are alike. They include integral link chains like flat top, welded steel chains and bar link.
Application of Chain Drive
- Wood working machinery.
- Power transmission.
- Transportation industries.
- Agricultural machinery.
- Oil well drilling rigs.
- Material handling equipment.
- Building construction.
- Lifting loads.
Uses of Chain Drive
1. Bicycles
Chain drive was one of the prominent features in the safety which is introduced in 1885 and it have two wheels of equal sizes and it is still a very basic features provided in the design of bicycle.
2. Automobiles
In early time many cars uses chain drive but later it was replaced by rear axle with roller chains. It results in simple designs. Chains are long lasting but their replacement is harder.
3. Motorcycles
Use of chain drive or driveshaft or belt drive is basic requirement in motorcycle design. Almost all motorcycle design have one of these components.
Advantages of Chain Drives
- Use of chain drive is suitable for long as well as short distance.
- From a single chain various numbers of shafts are driven.
- Overall dimensions of chain drive are small and are compact.
- They do not cause fire hazard.
- Environment conditions and the temperature do not affect working of the chain drive.
- Initial tension is not required by the chain drive.
- Their efficiency is very high almost around 96 percent.
- Slip does not occur in chain drive.
- They can be easily installed.
- Abrasive conditions are also be withstand by chain drive.
- Their operation can also be done in wet conditions.
Disadvantages of Chain Drives
- Cannot be used at the place where slip occurs.
- In compare to belt drives they need more precise alignment.
- Frequent lubrication is needed.
- In compare with gear drives they have less load capacity.
- Operation of chain drive is noisy and they cause vibration.
- For non parallel shafts they are not suitable.
- Chain drives cannot be used to the place where precise motion requirement.
- Chain drives need housing.
- Chain drives need adjustment for slack such as tensioning device.