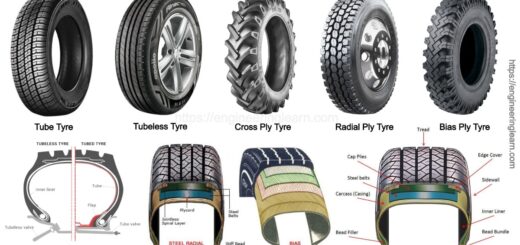
What is Catalytic Converter?
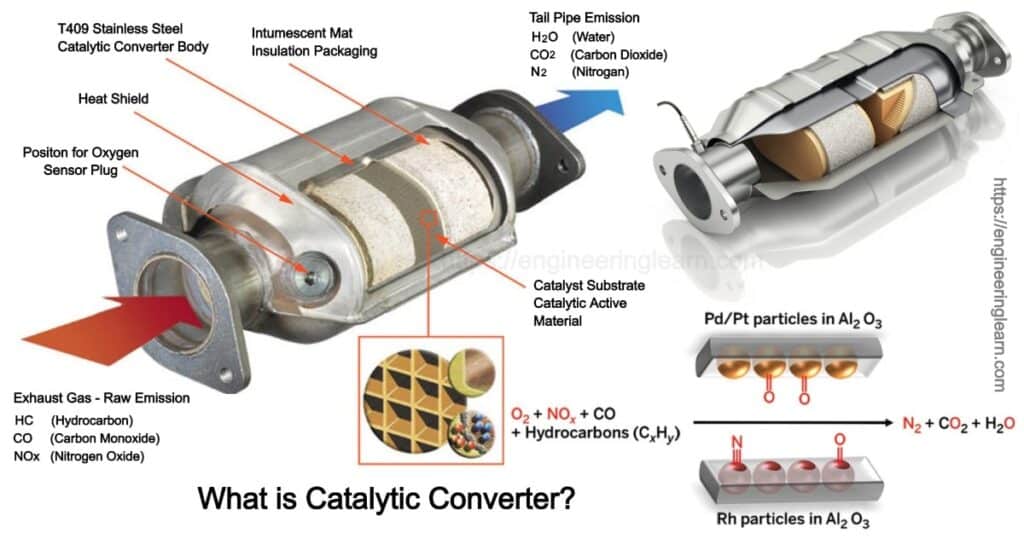
What is Catalytic Converter? :- If we talk in a scientific or a technical language then a catalyst can refers to as a chemical which is used in a chemical reaction to make the reaction go faster without changing itself in the whole process. The same is the work of a catalytic converter wherein the catalyst’s job is to speed up the removal of the pollution.
The gases which are found causing pollution are made of various harmful molecules which are made from relatively harmless atoms. So, if there could be a process of splitting up the molecules once they leave the engine of the car and before they get pumped out into the atmosphere. We could definitely resolve the problem of pollution or can take out an alternative. This is the main work which a catalytic converter is supposed to do.
Specification of Catalytic Converter
A catalytic converter is basically a metal box which is bolted under the car, with two pipes coming out of it. One amongst them is the input of the converter and is connected to the engine which brings in hot and polluted fumes from the cylinder of the engine in order to produce power. The other pipe which can refer to as the output of the converter is connected to the tailpipe or the exhaust which is used to blow over the fumes from the engine, breaking the pollutant gases and converting them into safe and harmless gases which can be blown out into the air easily.
It is very important to know that the catalytic converters are those which require you to use the unleaded fuel as the lead is a conventional fuel or must be called as poison which the catalyst prevents from taking up the pollutants in the exhaust gases.
What Happens Inside The Converter?
In the converter there are various gases involved which flow through a dense honeycomb structure that is made from ceramic and is coated with the catalysts. The structure lets the gases touch a quite bigger area of the catalysts at once, with the help of which they are converted quickly and with full efficiency. There are two different types of catalysts which are present inside a catalytic converter
- One catalyst deals with the pollution caused by nitrogen oxide with the help of a chemical process of removing oxygen which is also well known as reduction. This process breaks up the nitrogen oxides into nitrogen and oxygen gases in order to make it harmless, as it already exists in the air available in surrounding.
- The second catalyst works with an opposite chemical process which includes the addition of oxygen which is referred to as oxidation which converts the carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide. The oxidation reaction gets converted into an unburned hydrocarbon in the exhaust itself.
It is important to know that there are three different types of chemical reactions which take place at the same time. This is the reason they are termed as three-way catalytic converters. Once the job allotted by the catalyst has been done it emits gases like nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water in the form of steam.
Working of Catalytic Converter
In the ancient era when there were no catalytic converters, the gases which were waste and were produced by the engine of the cars were blown directly into the tailpipe and were then released to the atmosphere. The catalytic converter is set within the engine and the tailpipe, but it is important to know that it does not work like a normal filter rather it changes the chemical composition of the exhaust gases by simply rearranging the atoms by which they are made:
- The molecules of the harmful gases are pumped from the engine.
- The catalyst is used to split up the molecules into atoms.
- These atoms recombine into molecules of harmless substances like carbon dioxide, nitrogen and water, which blows out safely from the exhaust.
How Effective Are Catalytic Converters?
The main aim for designing a catalytic converter was to reduce the immediate effect of local and dirty air where the car is being driven. The problem which is faced is that the temperature at which it works efficiently is over 300°C, which seems to happen when the engine has provides with a chance to get warmed up. In the ancient time the catalytic converters usually took around 10–15 minutes to warm up, so that they can remain ineffective for the first few kilometres of the journey. Whereas the modern converters warm up in very quickly in around 2–3 minutes, wherein the significant emissions can still occur during this time.
How Effective Are Catalytic Converters?
One more issue which arises is that the poisonous emissions increase the effect of the greenhouse gas. Most of us find carbon dioxide as a safe gas, whereas it is found toxic, not entirely, because we now know it is the major cause of global warming and climate change accompanied by some more gases. It is believed that the catalytic converters are also responsible for the climate change as they turn the carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide. The carbon monoxide gets converted in carbon dioxide eventually which is them released into the atmosphere by itself, therefore, a catalytic converter does not make any difference but, simply reduces the carbon monoxide which a car emits, into the atmosphere intending to improve the quality of the air.
When it comes to consider the causes of the climate change, then it must be said that the engineers and environmentalists have mentioned various other issues which have are found to be serious. A greenhouse gas is over 300 times more powerful than the carbon dioxide. The constraint faces is that there are numerous vehicles moving on the road which adds up a high amount of nitrous oxide leading to a serious concern. The use of catalytic converter as a measure of pollution control in the major industries, results in a substantial increase in emission of nitrogen dioxide from the gasoline vehicles.