Types of Engines
Types of Engines :- The engine is a device that converts the heat energy of fuel into mechanical energy. The engines are mostly used in the automobile industry. Different kinds of engines are available based on our requirements.
The major distinction between engines is 1) Internal Combustion Engine 2) External Combustion Engine.
Internal Combustion Engine
As the name suggests that in an Internal Combustion Engine combustion of fuel takes place inside the engine. The most common type of IC Engine is the four-stroke engine which has four different steps.
- Injection of fuel and oxidizer (Air) mixer inside the engine.
- Compression of Mixer.
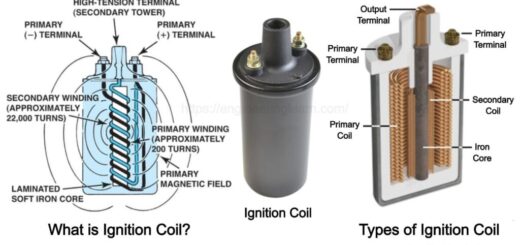
- Ignition of Fuel mixer by a spark.
- Rejection of exhaust.
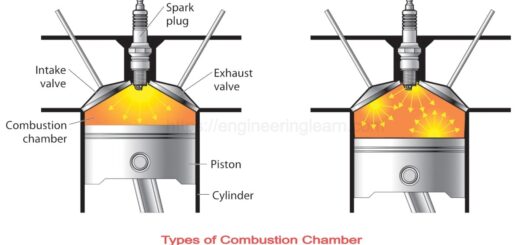
In this engine, fuel enters inside the combustion chamber and the piston compresses it. Due to compression and spark ignition, high pressure and temperature impart on the piston which is used to rotate crank which is connected to the piston via a connecting rod.
External Combustion Engine
As the name suggests that in an External Combustion Engine combustion of fuel takes place outside the Engine. Here the extra heat is utilized to produce low-pressure steam which is used in the turbine to produce electricity. Here the fuel is burnt outside the engine so we can also use solid fuel.
Now let’s talk about different types of engines based on different criteria:
Based on Design:
1. Reciprocating Engine (Piston Engine): ( Types of Engines )
In this type of engine piston-cylinder assembly is given. Piston moves to and for inside the cylinder. This is the most common type of engine used in the automobile industry.
2. Rotary Engine (Wankel Engine): ( Types of Engines )
In this type of engine instead of the piston there is a rotor that rotates the wheel of the vehicle. It is invented in 1957 but is currently not used by people. The pressure generated by fuel combustion is imparted on the rotor.
Based on the number of Strokes:
1. Four strokes Engine: ( Types of Engines )
In this engine, the piston moves two times up and down and the crank rotates two times per single fuel combustion. This is a very efficient type of engine. It is used in bikes, cars, etc.
2. Two Strokes Engines: ( Types of Engines )
In these engines, the piston moves only once up and down. The crank rotates only once per single fuel combustion.
Based on Fuel Used:
- Diesel Engine: Uses Diesel as fuel. Ex. Bus, Truck, etc.
- Petrol Engine: Uses Petrol as fuel. Ex. Car, Bike, etc.
- Gas Engine: Uses LPG or CNG gas as fuel. Ex. Auto, etc.
- Electric Engine: Uses electric energy to rotate the crank. Ex. Car.
Based on the Method of Ignition:
1. Compression-Ignition Engine: ( Types of Engines )
Here no extra equipment is used to ignite the fuel. Due to compression of fuel temperature increases which causes ignition of fuel.
2. Spark-Ignition Engine: ( Types of Engines )
Here to ignite fuel we use a spark plug. Due to this, it is called a spark-ignition engine.
Based on the number of cylinders:
1. Single-cylinder engine: ( Types of Engines )
Here we use only one the cylinder and piston assembly that is connected to the crank.
2. Multi-cylinder engine: ( Types of Engines )
Here we use more than two cylinders and a piston assembly and that is connected to the crank. The figure is shown below.
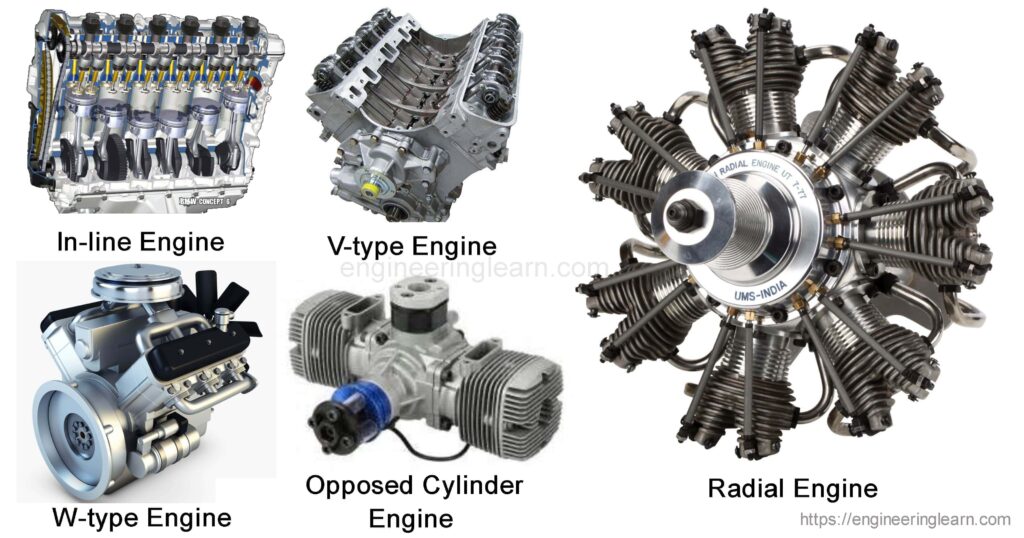
Based on the arrangement of cylinders:
- In-line Engine: Here cylinders are arranged in a single line along with the crankshaft.
- V-type Engine: Here cylinders are put at an angle along with the crankshaft.
- Opposed cylinder engine: Here cylinders are at an angle of 180o. Same as V-type but and 180o angle.
- W-type Engine: Here cylinders are the same as V-type but it has three cylinders pr single crankshaft.
- Radial Engine: Here cylinders are all around the shaft as shown in the figure.