How do Steam Engine Work
How do Steam Engine Work :- Steam engines are the engines which were well known for their performance and built quality and deserved to be remembered well as they swept the world during the Industrial Revolution of 18th and 19th century. Steam engines are ranked as one of the greatest inventions till date. These engines are the perfect example of machinery and engineering.
What Powers A Steam Engines?
Till the early 20th century, coal was one of the most favorite fuel and was used in everything like trains, ships and steam planes which was invented by an American scientist named Samuel P. Langley, who was an early rival of the Wright brothers. The best thing about coal was that it was available in bulk inside the Earth and therefore it was comparatively inexpensive and widely available.
Have you ever what exactly coal is? Coal refers to an organic chemical, which is based completely on the carbon element. Coal is found forming over millions of years ago due to the dead remains of the plants and animals which got buried under the rocks, squeezed by pressure or cooked by the internal heat of the earth. This is the reason why it is termed as a fossil fuel.
Steam engines required plenty amount of coal to move as coal contains half the energy per kilogram as compared to some fossil fuels like gasoline, diesel, and kerosene.
Step By Step Working Of A Steam Engine
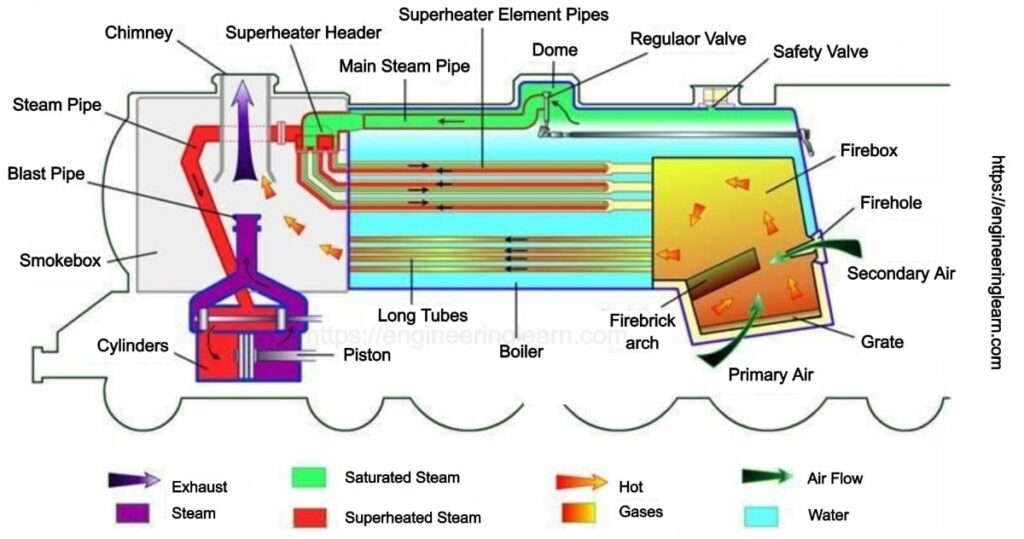
It is interesting to note how things work in a steam locomotive. Inside the steam engine, the coal is loaded into the firebox which is a sort of metal box that contains a coal fire. The fire on the coal heats up the boiler inside the locomotive which gives a movement to the engine.
The boiler of a steam locomotive does not look like a kettle, but it works on the same principle by producing steam under high pressure. The boiler has a big tank of water which can withstand dozens of metal tubes running through it. The tubes move from the firebox to the chimney, which carries the heat and smoke of the fire along with them. The arrangement which is made from the boiler tubes, which means that the engine’s fire can heat the water in the boiler tank very fast, in order to produce steam really quickly and with full efficiency. The water which is used to makes steam either comes from the tanks which are mounted on the side of the engine or is extracted from a separate wagon known as tender which is pulled behind the locomotive.
The steam which is generated in the boiler flows down into the cylinder just ahead the wheels, which pushes the plunger and the piston back and forth. There is a little mechanical gate inside the cylinder, which is known as the inlet valve made to let the steam in. The piston which is responsible for the movement is connected to the wheels of the locomotive with the help of an arm elbow shoulder joint known as crank and connecting rod.
How do steam engines work?
Once the piston pushes the crank and connecting rod, it turns the wheels of the engine and gives power to the train. Once the piston has reached near the end of the cylinder then it cannot be pushed further. This tendency of keeping the train in movement carries on the crank by pushing the piston back into the cylinder from where it had actually displaced. After this the steam inlet valve gets closed. The outlet valve opens when the piston moves the steam back through the cylinder from the chimney of the engine. The noise made by the steam engine, and the smoke caused when the piston moves back and forth in the cylinder.
There is a cylinder fit on the either sides of an engine and both these cylinders fire slightly out with respect to the other one to ensure that there is always some power pushing the engine along with it.
One-cylinder steam engine is used as a steam locomotive down a track which is called a rotary steam engine due to the function of the piston to make the wheel rotate. Earlier, the steam engines worked in a completely different manner by just pushing the piston up and down in a simple back and forth motion. The reciprocating steam engines were brought into use to pump out water from the flooded coal mines in the ancient era.
Single-Acting Steam Engine
These are the engines which the steam pushes the piston in a single direction and the momentum of the locomotive drives it the other way. But this was found to be the most inefficient design as the piston is powered only half the time.
Double Acting Steam Engine
These are a slightly complex engines but are much better as it uses extra steam pipes and valves to make the steam move the piston initially in one way and then in the other. This is also named as counter flow steam engine.
The reason why it is more powerful is as the steam drives the piston for the whole time. If the wheels of a typical steam engine are observed properly, it will be noted that each and every part is quite complex than it is seen in the images as there is much more complexity in the engine than just a single crank or a connecting rod. It includes a collection of levers which are used to slide back and forth with accuracy. This is also known as valve gear.
The main job of it is to open and close the valves of the cylinder at the correct moment which helps the steam to enter and exit in order to make the engine work efficiently and powerfully as much as possible which also allows it to move in reverse. There are various different types of valve gears. One of the most popular design amongst all is known as Walschaerts, which was named after a Belgian inventor Egide Walschaerts