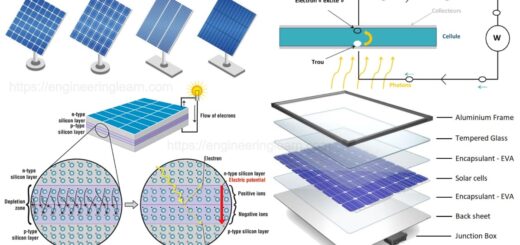
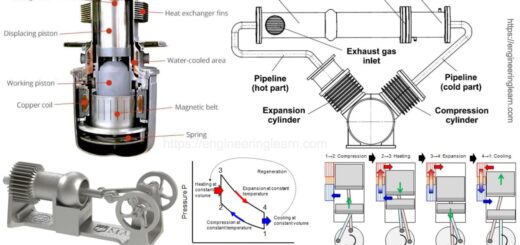
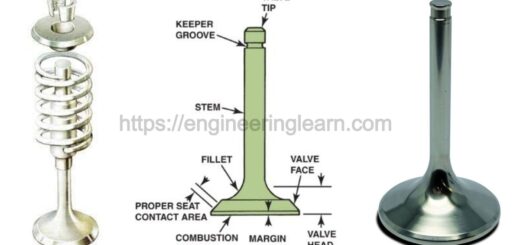
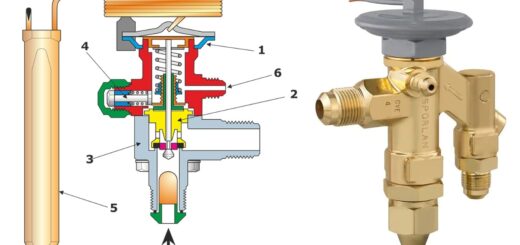
Gas Turbine Components and Principle
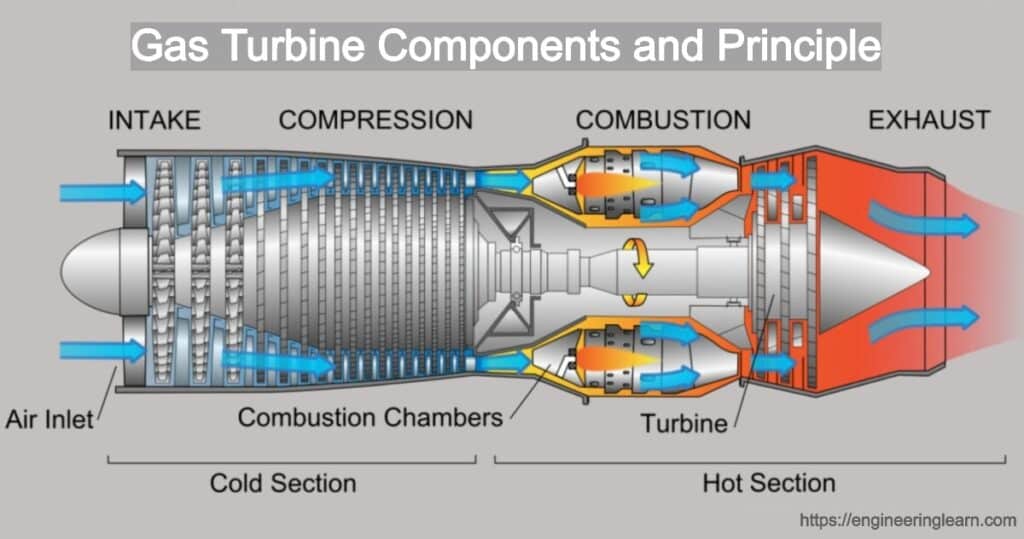
Gas Turbine Components and Principle :- A gas turbine is a type of internal combustion engine whose working fluid is the air itself. The engine is used to extract chemical energy from fuel and is also used to convert the chemical energy into the mechanical energy by the use of gaseous energy as the working fluid to drive the engine and propeller, this, in turn, propels the aircraft.
Gas Turbine Components
1. Inlet
The air should be kept flowing unrestricted from the duct and the inlet duct should also remain neat and clean in order to keep the engine healthy. It is suggested to provide clean and undisturbed airflow at the inlet which when supplied to the engine increases its efficiency and protects the engine from erosion, corrosion, or any damage.
It is also suggested that the fairings should be installed within the engine air inlet duct and the inlet duct to make sure that the airflow losses are minimum with respect to all the conditions of the airflow.
2. Compressor
The compressor is the one which is responsible for providing the turbine with the required amount of air which is needed to make it work in an efficient manner. In addition to this it is required to supply the air at a very high static pressure. The commonly known ratio of pressure at the back compressor to pressure at the front compressor is 9:5.
3. Diffuser
The air exits through the guide vanes of the compressor where the components of air flow gets converted into a straight-line flow. After this the air enters into the diffuser section which is a divergent duct. The basic function of a diffuser is aerodynamic.
4. Combustor
Once the air passes through the diffuser, it enters into the combustion section which is known as combustor. The combustion section has a task which controls the burning of fuel and air. The heat which is released must be in a manner that the air gets expanded and accelerated in order to provide a smooth and stable stream for a uniformly heated gas at all conditions of operation. It is mandatory to accomplish the task with a minimum pressure loss and maximum a heat release.
5. Turbine
A turbine engine has a four-stage turbine which is used to convert the gaseous energy of the air fuel into a mechanical energy to move the compressor with the help of a reduction gear or the propeller. The turbine has a function wherein the gaseous energy gets converted into the mechanical energy by expanding the hot and high-pressure gases into lower temperature and pressure.
6. Exhaust
Once the gas passes through the turbine, it gets discharged through the exhaust. Mostly the gaseous energy gets converted into mechanical energy by the help of a turbine, a sufficient amount of power remains in the exhaust gas. This remaining gas is accelerated through the convergent duct of the exhaust to make it more useful as the airplane drives.
Gas Turbine Working Principle
The basic principle on which the gas turbine works is identical to all the engines which is used to extract energy from the chemical fuel. The most commonly known 4 steps for any internal combustion engine are as follows:
- Air Intake.
- Air Compression.
- Combustion, where the fuel is injected and made to convert to the stored energy.
- Expansion and extinct, where the converted energy is brought to use.
In case of a piston engine like the engines used in the cars or as the airplane engine, the steps which are involved is the intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust in the cylinder head but at the different times as the piston continuously moves up and down.
In case of a turbine engine, the same four steps occur that too at the same time but at different places. Due to this fundamental difference the turbine has various engine sections which are known as:
- Inlet section
- Compressor section
- Combustion section
- Turbine and exhaust section.
The turbine section of the engine is responsible for producing the usable shaft power as an output which is used to drive the propeller. Other than this it must be provided with the power to drive the compressor and the engine accessories. This is done by the exposure to the high temperature, pressure, velocity gas which is converted from the gaseous energy to the mechanical energy in the form of a shaft power.